The digitization of financial services and the advent of open banking pose a series of game-changing implications for service providers and consumers alike. Correct compliance with the EU's revised regulatory framework, PSD2, is key for the successful transition of online payment service providers (i.e. banks and financial services firms) to API-led connectivity and a more competitive and innovative market. Guardsquare provides security solutions that fit within the Zero Trust security model and safeguard mobile apps against reverse engineering and tampering, as well as protect the Regulatory Technical Standards (RTS) implementation requirements for PSD2 compliance.
The following article sums up what PSD2 means for your apps and business, and how Guardsquare can help with compliance.
PSD2
Created in 2013 and in full effect by September 2019, PSD2 revolutionizes online payments by giving banks and non-banking third-party players (TPPs) access to consumer bank account information, while (1) enforcing higher security measures for consumer payments, (2) fostering innovation, and (3) encouraging competition among all service providers. PSD2 regulations facilitates the optimization and democratization of e-payment services, enhancement of customer experience, and retention. As PSD2 grants new access rights to TPPs and banks, it also enforces stricter security measures to consumer account information.
In short, PSD2 is responsible for two key changes for which implementation requirements are defined by the Regulatory Technical Standards (RTS):
- Provisions on Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) for online payments to provide an increased level of security of electronic payments. For mobile and remote payments, SCA must additionally be ensured by using a unique authentication code to dynamically link the transaction to a specific amount and specific payee.
- Common and secure open standards of communication (CSC) to safely share payment account data or initiate payment transactions, by (1) providing an API for secure information exchange and (2) adapting the customer online banking interface to provide access to TPPs.
How can Guardsquare help?
Protecting your financial transactions at the app level is the most effective way to prevent unauthorized access to your application’s services. As the leader in mobile application security, Guardsquare solutions help protect your SCA & CSC implementations by applying multiple techniques of code hardening & injecting runtime application self-protection (RASP) checks.
Our solutions help fulfill PSD2/RTS implementation requirements by correctly applying hardening techniques at critical code locations and threat detection through:
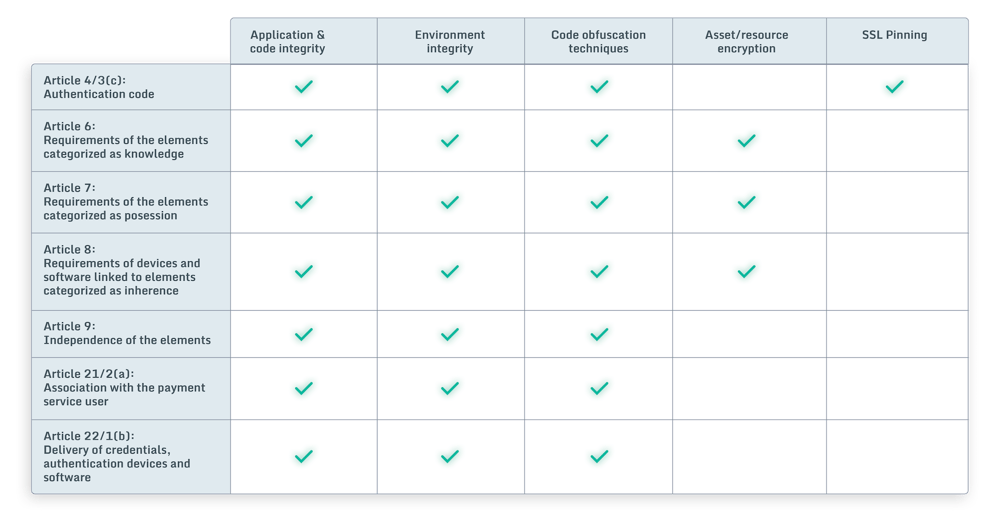
- Application and code integrity, to ensure the overall integrity of banking apps and SDKs.
- Environment integrity of the device(s) on which apps are run, via root/jailbreak, hook, debugging, emulator, and virtual environment detection.
- Code obfuscation techniques, to protect against reverse engineering and tampering during online payments.
- Asset/resource encryption, to protect app assets/resources including certificates, configuration files, etc.
- Data encryption, to protect API - & encryption keys from leaking during static analysis.
- Threat monitoring, to help identify users and devices generating threats that could lead to fraudulent transactions.
- SSL pinning hardening, to avoid bypassing the secure communication with the backend.
Conclusion
As mobile applications become a critical part of financial infrastructures, app security and compliance become imperative for any successful IT security model today, such as Zero Trust. Our software (DexGuard, iXGuard, and ThreatCast) help ensure the overall effectiveness of your IT security architecture by safeguarding your mobile endpoint. Ensuring app and platform integrity, through preventing reverse engineering and hacking, is also vital in protecting multiple points discussed in PSD2.
Our technical solutions fulfill specific PSD2/RTS requirements, such as obfuscation of critical code and resources used for unique identification, to prevent replication of the information used to uniquely identify the device; Software and platform integrity testing, to ensure a trusted/secure execution environment; Threat Monitoring, to help identify users and devices generating threats that could lead to fraudulent transactions.; SSL pinning hardening, to avoid bypassing the secure communication to the backend for eavesdropping or interception.






