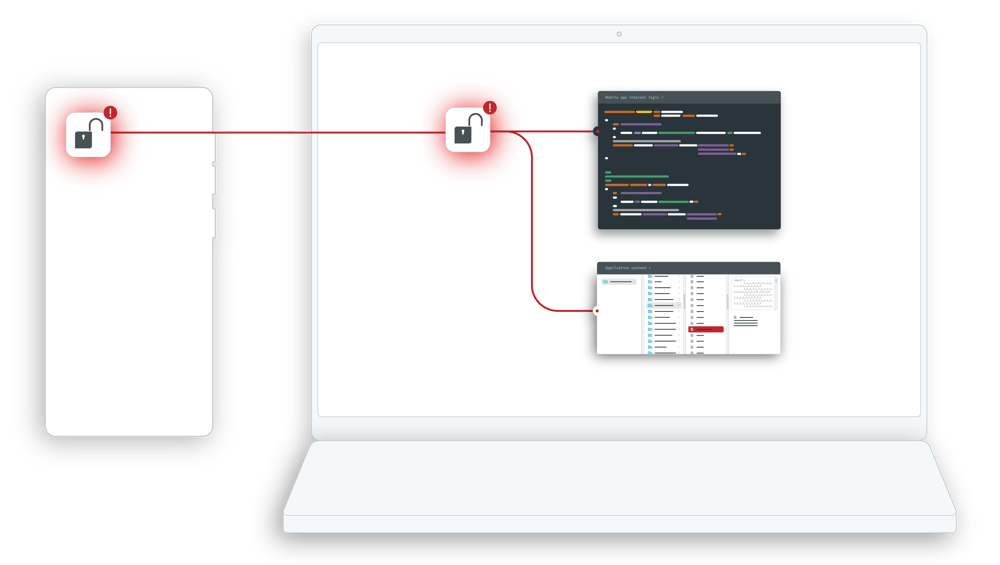
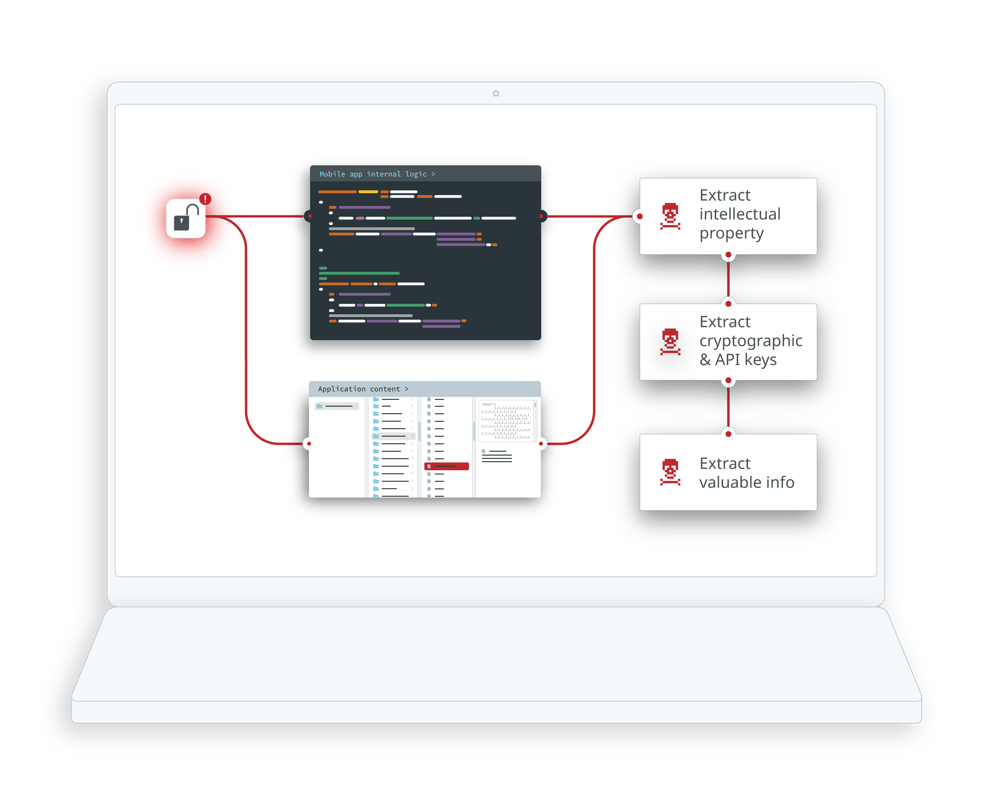
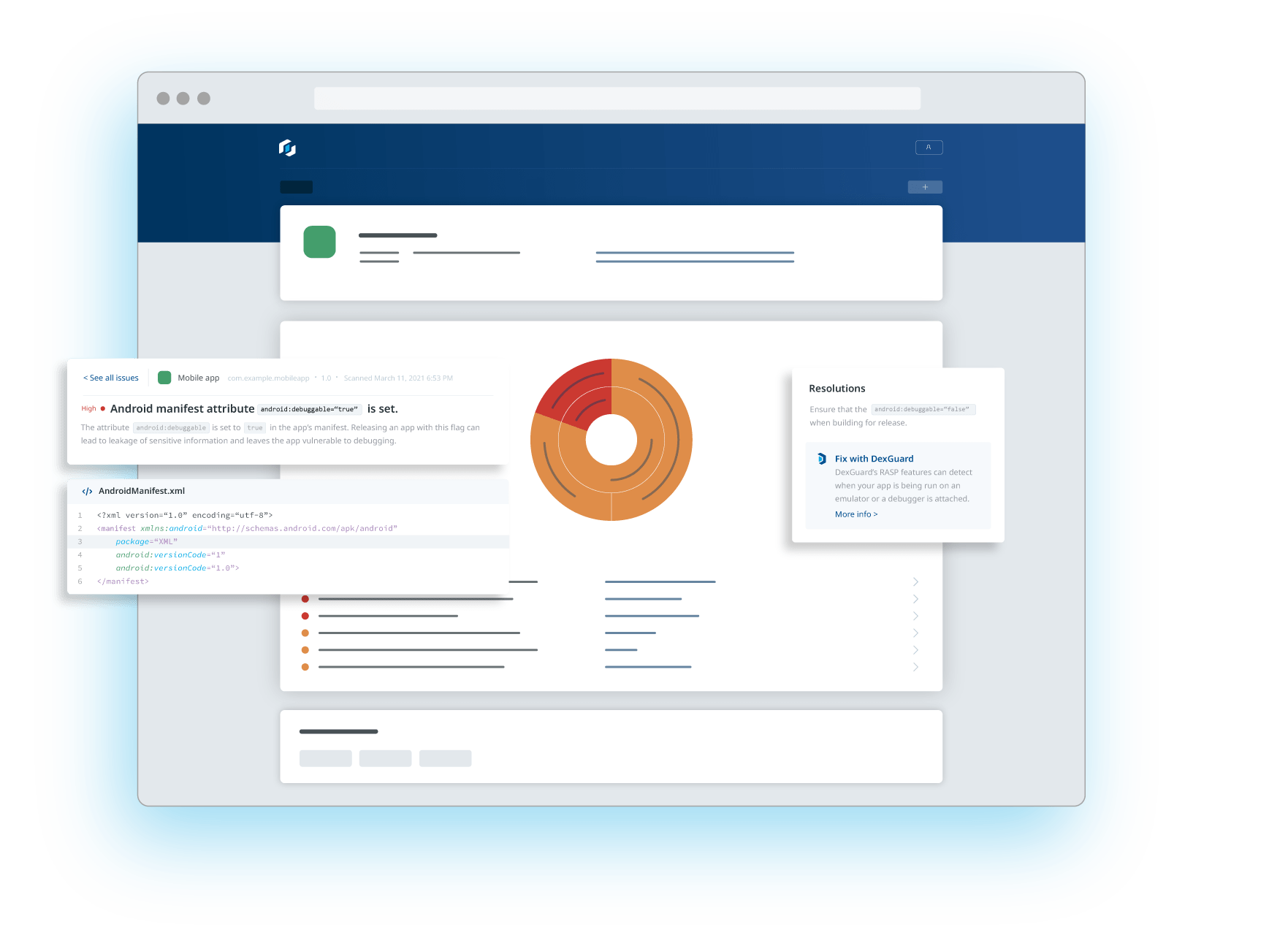
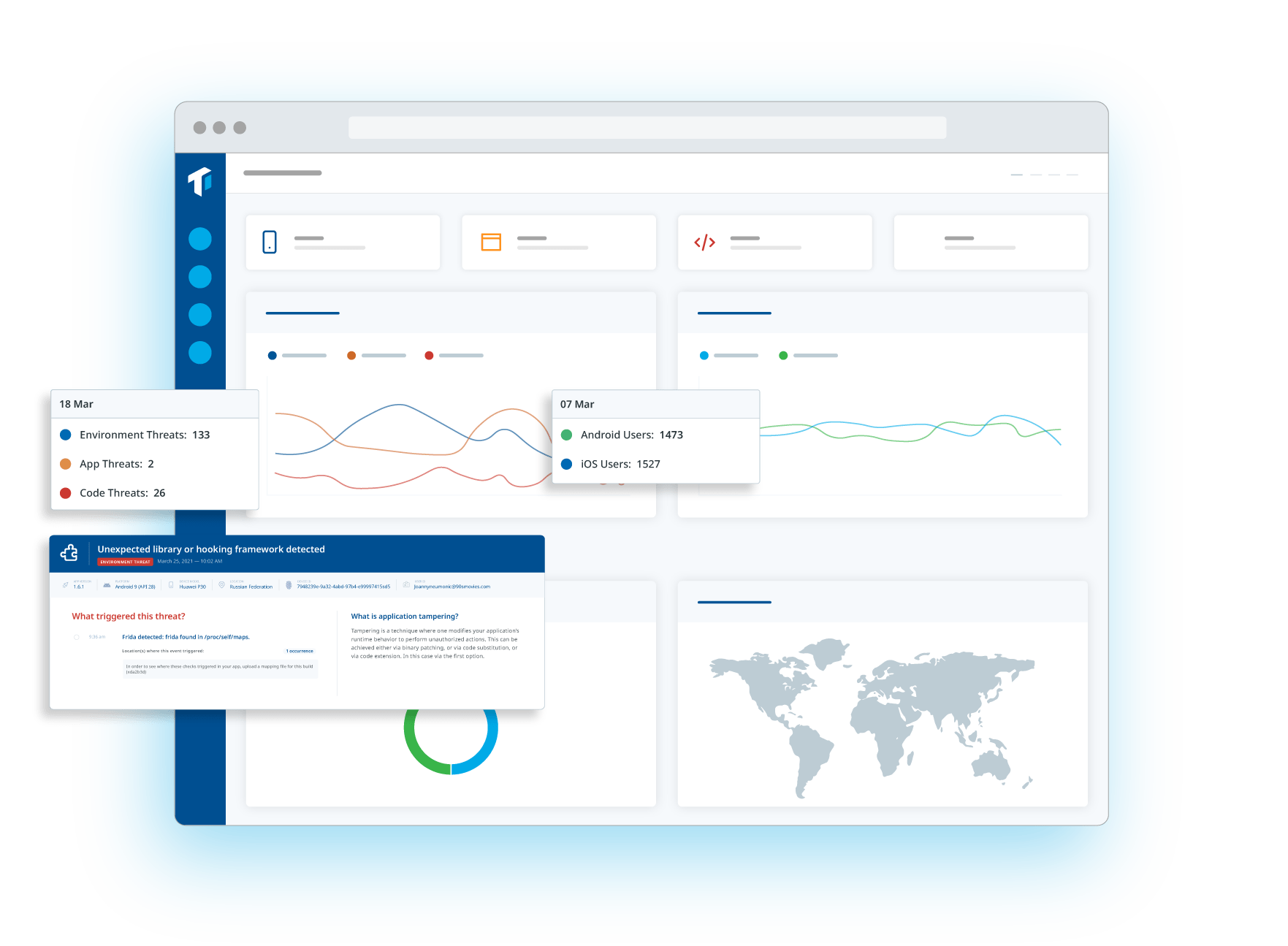
Mobile application code hardening is crucial in delaying tampering and reverse engineering attempts. It aims to create a robust defense against various security threats, including unauthorized access, data breaches, and the introduction of malicious code.
-
Products
-
Solutions
-
Resources
-
Company
- Pricing