!hooked
a technical magazine_
As a developer, how curious are you about
the security of mobile apps?
Code hardening is an abstract and deeply technical topic, making it difficult to get good hands-on knowledge and experience. That’s why our engineers created a set of fun and practical labs around four different application hardening techniques.
This technical magazine is the perfect way to improve your security knowledge in an engaging and practical way, no matter which mobile platform you use. Along the way, we'll dive into some low level compiler and security concepts to help you learn some interesting app hardening techniques.
Download all of the !hooked labs
Check out the first !hooked lab, it's free
Through the real world scenario of removing license checks from paid software, this lab explores how to protect mobile apps against binary patching by applying checksumming to the code. The lab explains the theory and explores a practical implementation for an iOS app, with corresponding code snippets and the aid of reverse engineering tools like radare2.

Who is !hooked for?
Developers busy creating mobile apps that are interested in learning more about the security aspect of app development such as code hardening.
Who wrote !hooked?
Our team of expert engineers, who work every day to deliver high-quality mobile security software, wrote this technical magazine to share their in-depth knowledge about how to best secure mobile applications.
Explore 3 additional !hooked labs
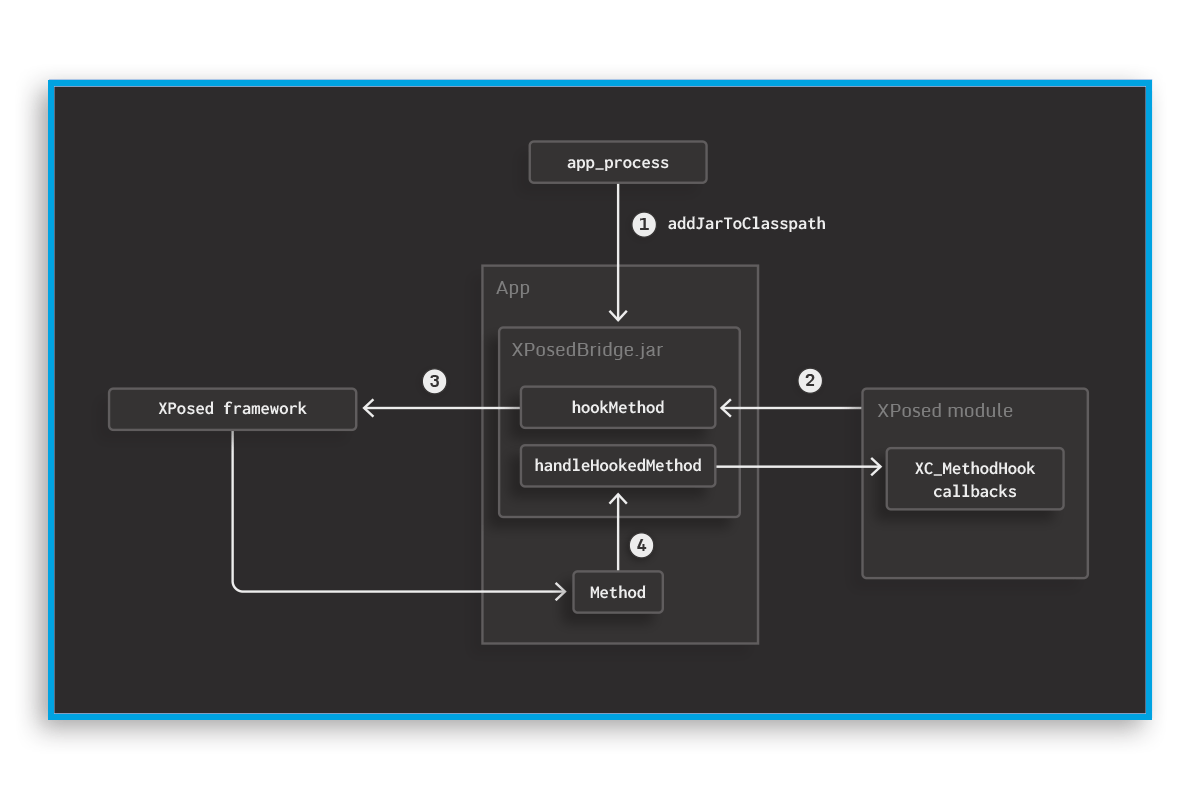
Defend apps against hooking during runtime.
With hooking, an attacker can observe how application code works while it runs, alter the control flow in various ways, or even change the behaviour of the code.
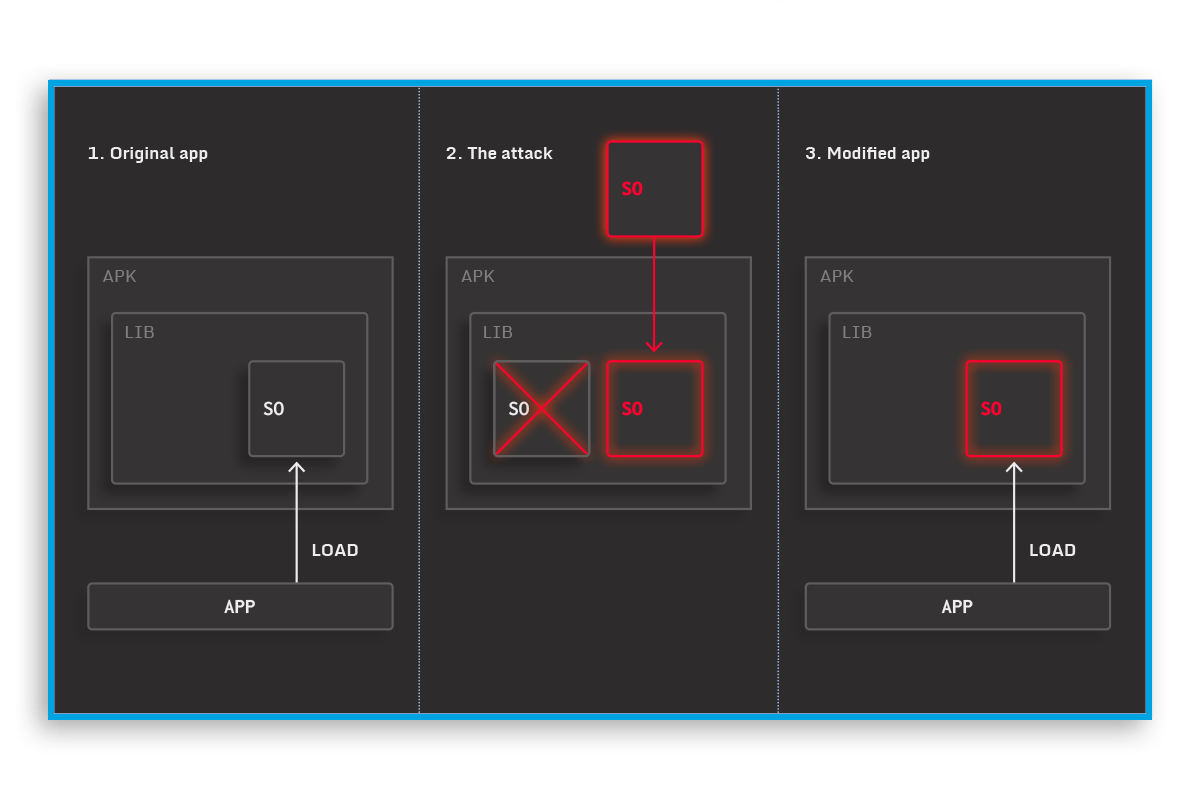
Mitigate the risk of native library analysis and replacement.
Native libraries speed up the execution of mobile apps; however, they also add an additional attack surface. By replacing them, a malicious actor can alter the app behaviour or even completely remove its functionality.
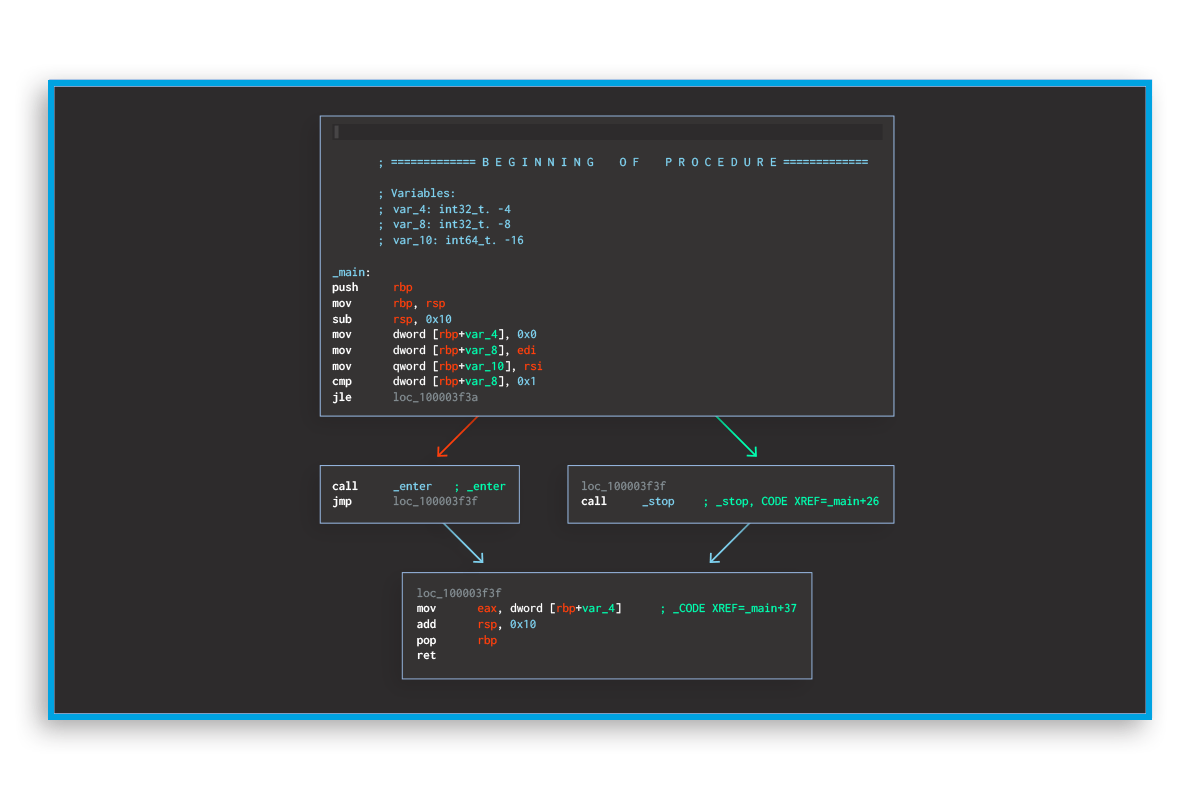
Make it harder to understand the function call graph within mobile apps.
By leveraging the function call graphs, an attacker can easily get insight into the control flow of an app, a crucial step in reverse engineering.

Defend apps against hooking during runtime.
With hooking, an attacker can observe how application code works while it runs, alter the control flow in various ways, or even change the behaviour of the code.

Mitigate the risk of native library analysis and replacement.
Native libraries speed up the execution of mobile apps; however, they also add an additional attack surface. By replacing them, a malicious actor can alter the app behaviour or even completely remove its functionality.

Make it harder to understand the function call graph within mobile apps.
By leveraging the function call graphs, an attacker can easily get insight into the control flow of an app, a crucial step in reverse engineering.







